Actions
The Actions feature in Elvin Copilot allows admins to configure external or internal functions that the copilot can call during a conversation. This enables API calls and system integrations that return data or perform defined operations.
Currently, Elvin Copilot supports the following types of actions:
- REST API Calls – Connect to and interact with any system that exposes a REST endpoint.
- JavaScript API Calls – Execute JavaScript functions within your application environment.
- HubSpot CRM Integration – Access customer records in HubSpot through a dedicated connector.
Creating a New Action
To create a new action:
- Navigate to Elvin Copilot → Connect → Actions.
- Click Create New.
- Select an Action Type (REST API, JavaScript API, HubSpot).
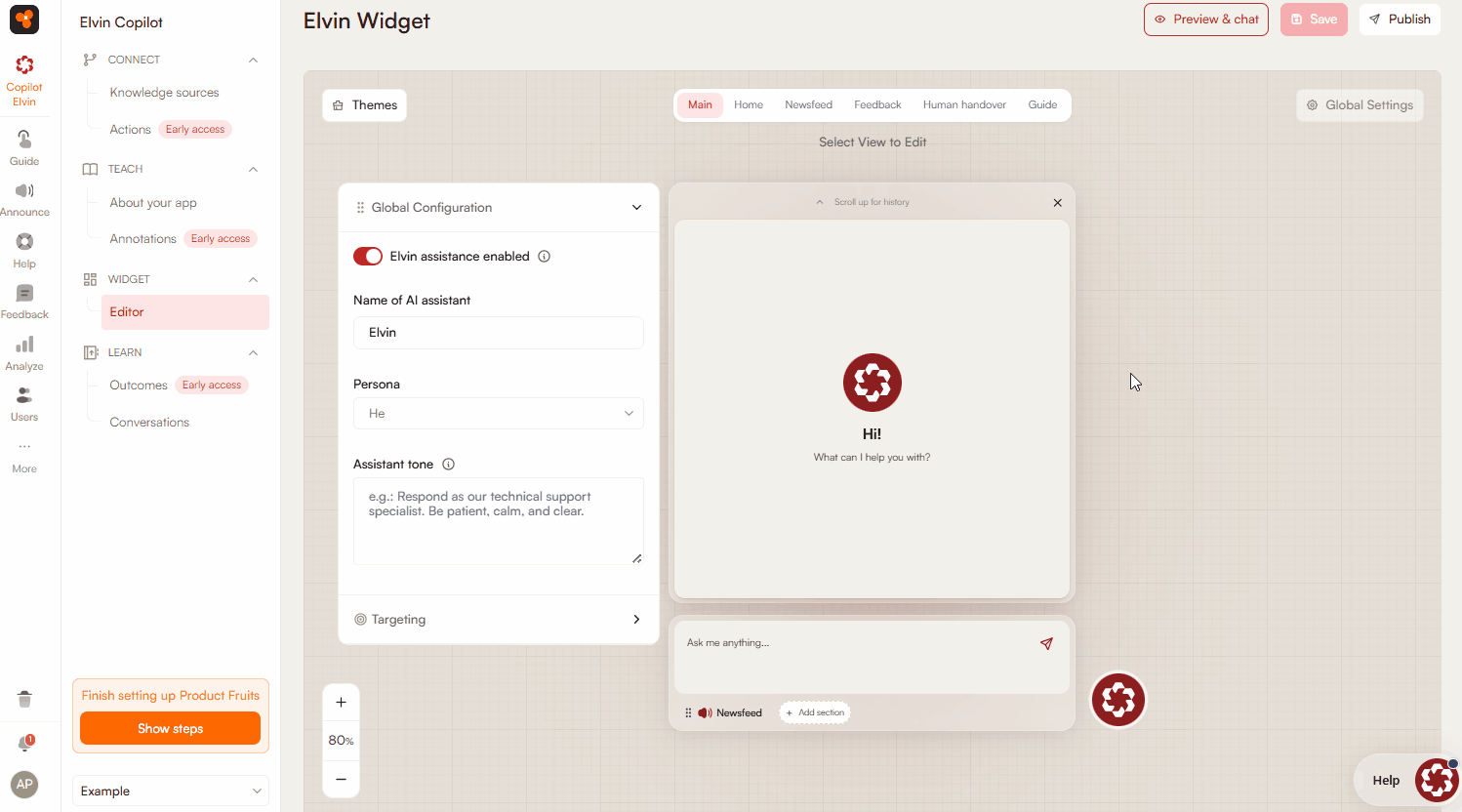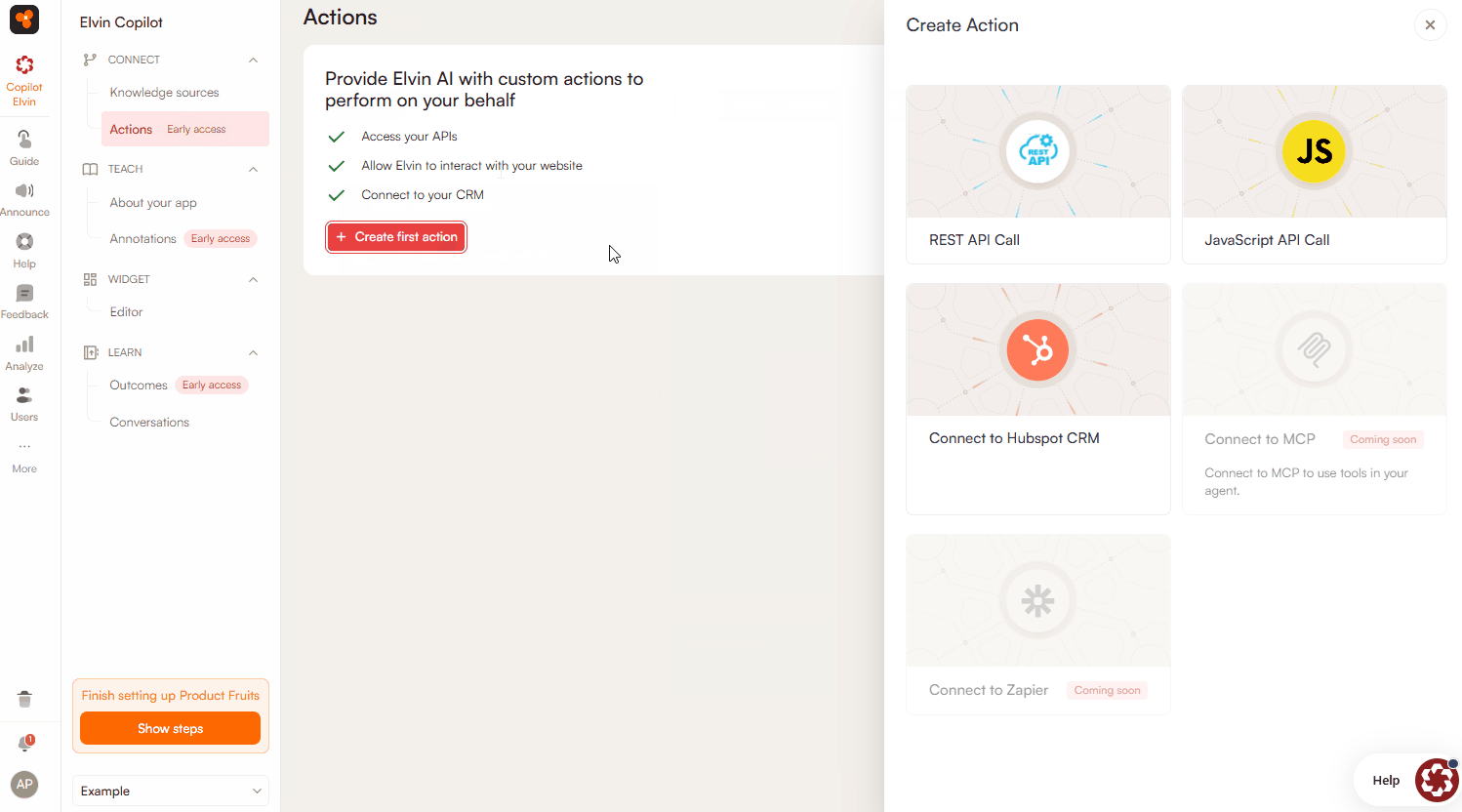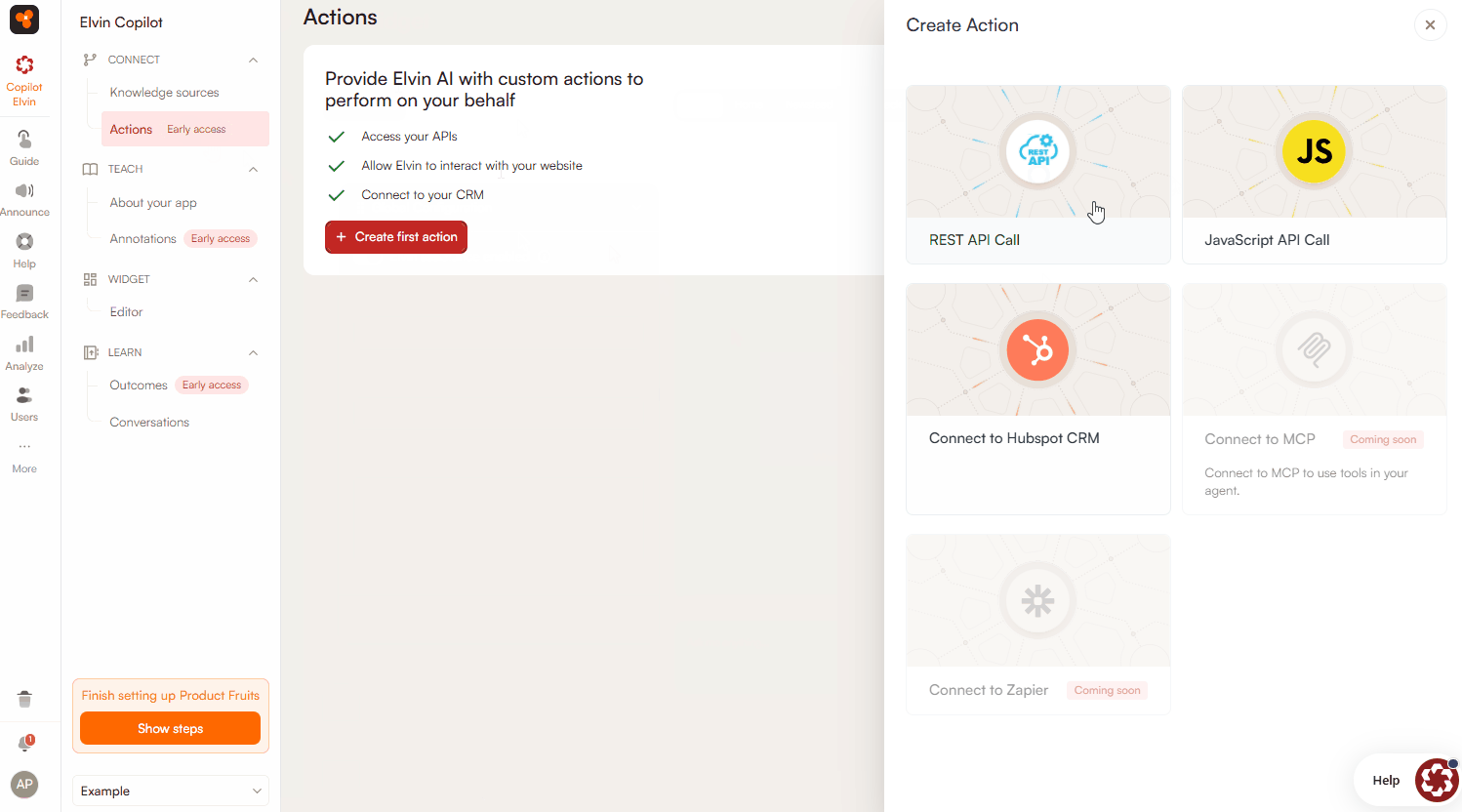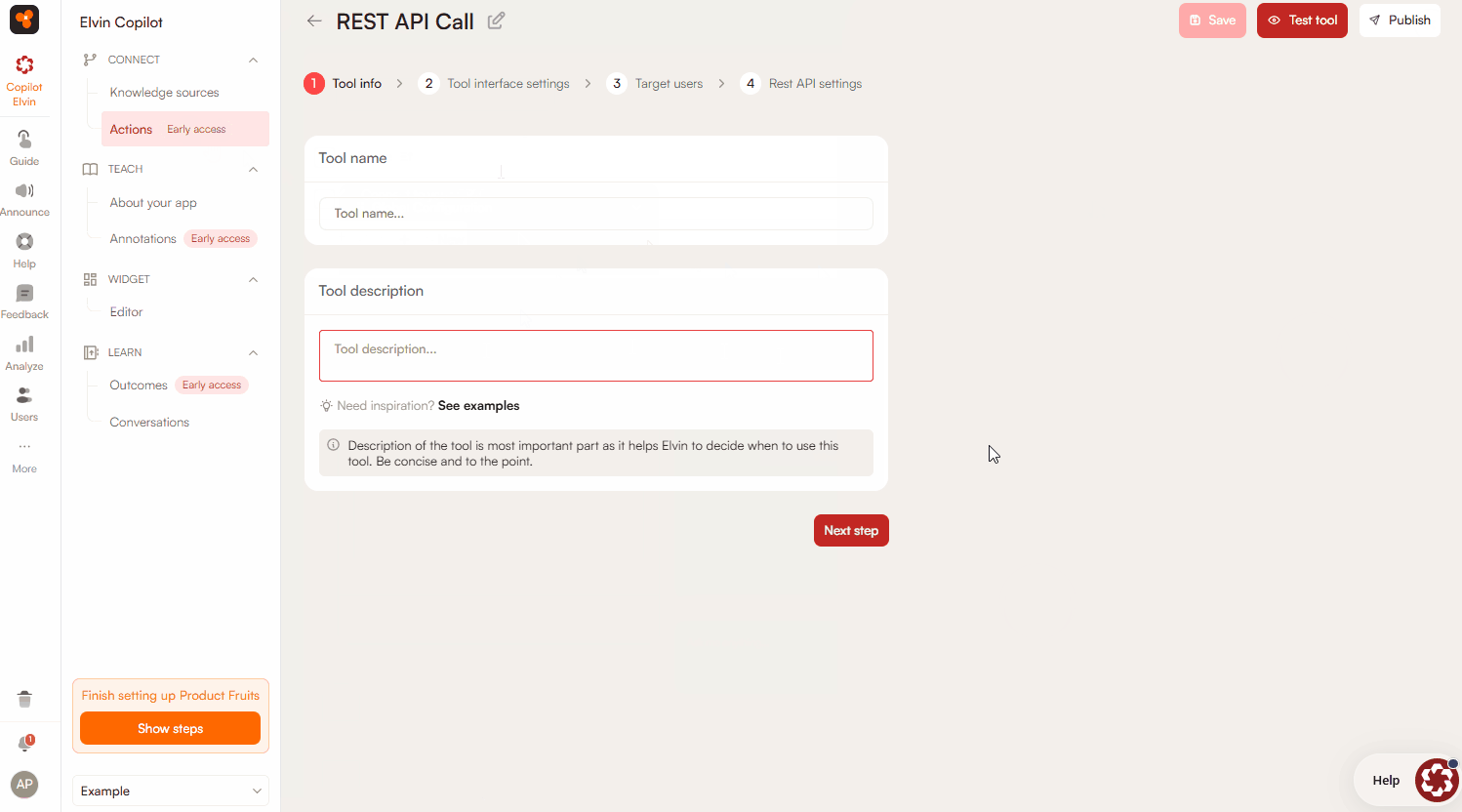
- Enter the Tool Name and Tool Description.
- Tool Name: a clear identifier for admins and the copilot.
- Tool Description: instructions on when and how the copilot should use the tool. Clear, specific descriptions are critical for correct usage.
Best Practices for Tool Descriptions
The tool description is one of the most important parts of configuring an action. If it is too vague, the copilot may either overuse the tool (calling it in situations where it shouldn’t) or underuse it (failing to call it when it would be helpful).
Defining Tool Arguments
In the next step, define the arguments required for the action:
- Name – Identifier for the argument.
- Type – Select from:
string,integer,long,double,boolean. - Argument Description – Explain the purpose of the argument.
- Default Value – Optional predefined value.
- Required – Check if the argument must be provided before the action can run.
Best Practices for Argument Design
Arguments should always have meaningful names and clear descriptions, so the copilot knows exactly how and when to use them.
Clear argument design ensures the copilot can make reliable calls without confusion or misfires.
Setting Targeting
Specify which end-users can access the action:
- All Users – Action available to everyone.
- Segment – Action restricted to a defined user group.
- Custom Rule – Action available only when specific conditions are met.
REST API Actions
For REST API actions, an additional Main Info tab is available:
- URL – Endpoint of the REST service.
- Method – Choose from
GET,POST,PUT, orDELETE. - Headers – Optional HTTP headers.
- Request Body – A JSON object sent to the REST API.
Using Variables in Request Body
You can insert variables into the request body:
- Variables are enclosed in double curly braces
{{ }}. - Variables are replaced with the actual value at runtime.
- Variables can come from tool arguments or user/workspace properties (e.g.,
{{user.name}},{{user.props.customProperty}}). - All values are JSON encoded. To insert a raw string, append
|raw(e.g.,{{user.name|raw}}).
Example Get Request
curl -X GET "https://api.example.com/v1/customers?limit=10" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer {{user.props.apiToken}}" \
-H "Accept: application/json"Example Post Request
curl -X POST "https://api.example.com/v1/customers" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer {{user.props.apiToken}}" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"name": "{{user.name}}",
"email": "{{user.email}}"
}'Authentication Patterns
- API key header:
H "x-api-key: {{user.props.apiKey}}" - OAuth 2.0 bearer:
H "Authorization: Bearer {{user.props.accessToken}}"
Error Handling
{
"error": "invalid_request",
"message": "The email field is required."
}Timeouts and Retries
- Recommended timeout: 30s
- Retries should use exponential backoff for
429or503responses.
PII Cautions
Avoid logging personally identifiable information (e.g. emails, phone numbers). Use redaction:
"email": "ali***@example.com"
HubSpot Actions
The HubSpot connector allows Elvin Copilot to integrate with your HubSpot CRM. At this stage, the integration is read-only. This means the copilot can retrieve customer information (for example, contact details or record properties) but cannot create, update, or delete records in HubSpot.
Future updates will expand functionality, but for now, HubSpot integration should be considered a safe way to expose customer data to the copilot without risking accidental changes.
Field Mapping Example
| HubSpot Field | Copilot Field |
|---|---|
| firstname | name |
| hs_object_id | id |
Monitoring Action Statistics
Under the Statistics tab, admins can review usage details for each action:
- Total Uses – Number of times the action has been called.
- Last Used – Timestamp of the most recent call.
- Last Use Took – Execution time of the most recent call.
- Last Use Was Error – Indicates whether the most recent call failed.
Search and Filter
You can locate specific actions using the search and filter options. Actions can be searched by typing their name into the search bar. Filtering is available through two categories: status and last updated. Status options include draft, pending changes, and published. The last updated filter allows selection of a predefined time interval such as the last 7, 30, 90, or 365 days, or a custom interval using the calendar selector.

 Need more help?
Need more help?